The healthcare industry relies on skilled professionals to diagnose and monitor heart conditions, and Certified Cardiographic Technician (CCTs) play a crucial role in this process. These specialists operate advanced cardiac testing equipment, assist physicians in detecting heart abnormalities, and contribute to life-saving patient care.
If you’re considering a career as a Certified Cardiographic Technician, this comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know—job responsibilities, required skills, certification pathways, career outlook, and steps to enter this rewarding field.
What Is a Certified Cardiographic Technician?
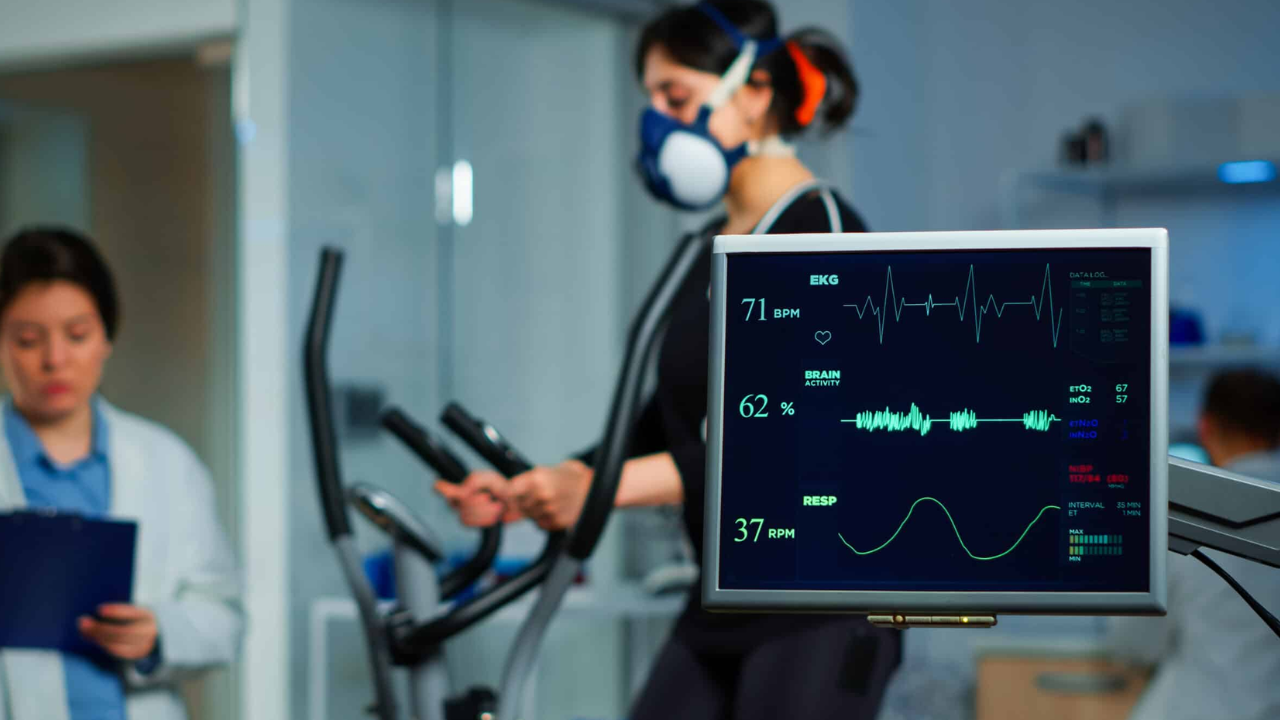
A Certified Cardiographic Technician (CCT) is a trained healthcare professional specializing in non-invasive cardiac diagnostic testing. They work closely with cardiologists, nurses, and other medical staff to perform tests that help detect heart diseases, arrhythmias, and other cardiovascular conditions.
Key Responsibilities
A CCT’s daily tasks may include:
- Performing electrocardiograms (EKGs/ECGs) – Recording the heart’s electrical activity to detect irregularities.
- Conducting stress tests – Monitoring heart performance during physical exertion (treadmill or stationary bike tests).
- Applying Holter monitors – Portable devices that track heart rhythms over 24-48 hours.
- Preparing patients for procedures – Explaining tests, positioning electrodes, and ensuring comfort.
- Maintaining equipment – Calibrating machines and troubleshooting technical issues.
- Documenting results – Providing accurate reports for physicians to interpret.
Work Environments
Certified Cardiographic Technician typically work in:
- Hospitals (emergency rooms, cardiology departments)
- Cardiology clinics
- Diagnostic laboratories
- Outpatient care centers
- Mobile cardiac testing units
How to Become a Certified Cardiographic Technician
Becoming a CCT requires a combination of education, hands-on training, and certification. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown:
1. Meet Basic Educational Requirements
- High school diploma or GED (minimum requirement).
- Recommended courses: Biology, Anatomy, Physiology, or Healthcare Fundamentals (helpful for certification exams).
2. Complete a Training Program
While some technicians receive on-the-job training, most employers prefer candidates who have completed an accredited cardiographic technician program. Options include:
- Certificate Programs (3-12 months) – Focused on EKG technology, cardiac anatomy, and diagnostic procedures.
- Associate Degree Programs (2 years) – Includes broader medical training, such as patient care and medical terminology.
3. Gain Clinical Experience
Many training programs include externships or clinical rotations, allowing students to practice:
- ECG electrode placement
- Stress test administration
- Patient interaction & safety protocols
4. Obtain Certification
Certification is not always legally required, but most employers prefer credentialed technicians. The two main certifying bodies are:
A. Cardiovascular Credentialing International (CCI)
- Offers the Certified Cardiographic Technician (CCT) credential.
- Exam covers:
- EKG interpretation
- Cardiac anatomy & physiology
- Stress testing & Holter monitoring
- Medical ethics & safety
B. American Health Credentialing Alliance (AHCA)
- Provides the Certified EKG Technician (CET) certification.
- Focuses on basic and advanced EKG skills.
Passing one of these exams boosts job prospects and earning potential.
Essential Skills for Success
Beyond technical knowledge, successful CCTs possess:
✔ Attention to Detail – Accurate electrode placement and test interpretation are critical.
✔ Communication Skills – Must explain procedures to nervous patients.
✔ Problem-Solving Abilities – Troubleshooting equipment issues quickly.
✔ Compassion & Patience – Working with patients who may be anxious or in pain.
Career Outlook & Advancement Opportunities
Job Growth & Demand
With heart disease remaining a leading health concern, the demand for cardiac diagnostic technicians is expected to remain steady. Hospitals, clinics, and mobile health services all need skilled CCTs.
Salary Expectations
- Entry-Level: $35,000 – $45,000 per year
- Experienced Technicians: $45,000 – $60,000+
- Specialized Roles (e.g., Cardiac Cath Lab Techs): Higher earning potential
Career Advancement Paths
With additional training, CCTs can specialize in:
- Cardiac Catheterization Technology
- Echocardiography (Echo Tech)
- Cardiovascular Technologist (CVT)
- Healthcare Management or Education
FAQs About Certified Cardiographic Technician
1. How long does it take to become a Certified Cardiographic Technician?
- Certificate Program: 3-12 months
- Associate Degree: 2 years
- Certification Exam Prep: 1-3 months
2. Is certification mandatory?
- No, but most employers prefer certified technicians for better job opportunities.
3. What’s the difference between a CCT and an EKG Technician?
- EKG Techs primarily perform electrocardiograms.
- CCTs have broader training in stress tests, Holter monitoring, and advanced cardiac diagnostics.
4. Can I study online?
- Yes, many schools offer hybrid programs (online theory + in-person clinical training).
Final Thoughts
A career as a Certified Cardiographic Technician offers job stability, competitive pay, and the satisfaction of contributing to patient care. By completing an accredited program, gaining hands-on experience, and earning certification, you can enter this field in under a year and grow into advanced cardiac specialties.
Ready to take the next step? Research accredited CCT programs and start your journey toward a fulfilling healthcare career today!